Map between a coding space (genotype), and another space, called the phenotype. These appear, for instance, in Evolution.
See MMathPhys oral presentation
Distribution of genotype network sizes in sequence-to-structure genotype–phenotype maps – Structural properties of genotype–phenotype maps
The structure of the genotype-phenotype map strongly constraints the evolution of non-coding RNA – Genetic Correlations Greatly Increase Mutational Robustness and Can Both Reduce and Enhance Evolvability
Types of GP relation
- Genetic dominance – Mode of inheritance. Traditional picture applies only sometimes, to traits called Mendelian traits. Modern picture shows it can all be much more complicated: partial dominance, pleiotropy, etc.
- Pleiotropy. Genes that affect many traits.
- Epistasis. Gene whose effect depends on other genes.
Structure of the GP map

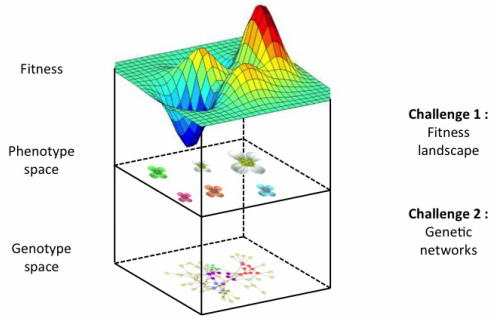
Genotype–phenotype mapping and the end of the ‘genes as blueprint’ metaphor
Distribution of genotype network sizes in sequence-to-structure genotype–phenotype maps
Developmental encoding or indirect encoding: you encode the instructions to build the system (by Morphogenesis), instead of the system itself (direct encoding). See Neuroevolution: Direct and Indirect Encoding of Networks. Comparing direct and developmental encoding schemes in artificial evolution
Genotype-phenotype maps - Stadler Ideas extending standard topology to explore the spaces defined by GPMs
Evolving scalable and modular adaptive networks with Developmental Symbolic Encoding Ideas of evolvable GPMs, evolving evolvability, etc.
Effects
Related concepts
Network topology of neutral networks
Topological Structure of the Space of Phenotypes: The Case of RNA Neutral Networks