Real-time PCR monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR process, i.e. in real-time, and not at its end, as in conventional PCR.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Real-time_polymerase_chain_reaction
Two common methods for the detection of PCR products in real-time PCR, all based on Fluorophores, are:
- non-specific fluorescent dyes that intercalate with any double-stranded DNA, and
- sequence-specific DNA probes consisting of oligonucleotides that are labelled with a fluorescent reporter which permits detection only after hybridization of the probe with its complementary sequence.
- SYBR Green
- TaqMan probe. These fluorescent reporters are non-fluorescent on the solution, but once they bind to the DNA, and Taq polymerase reaches them, the fluorescent group separates from the quenching group and becomes fluorescent.
- Molecular beacon
Primers
primer design programs have been developed for the production of amplicons with minimal potential for cross-hybridization (src)
Probes
SYBR Green

TaqMan probe
Most common
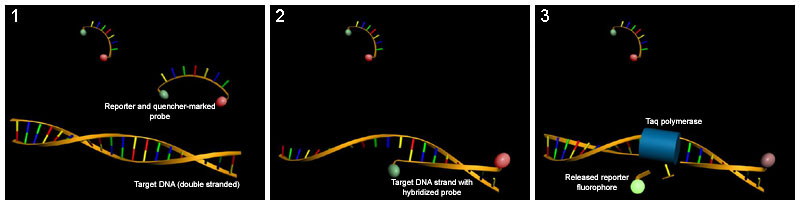 Functioning of the TaqMan probe sequence-specific fluorophore
Functioning of the TaqMan probe sequence-specific fluorophore
The advantage of this is that even if the probe binds to an incorrect strand, you also need the polymerase to break it, which requires the primer, which is also specific. This significantly reduces the probability of error over molecular beacons, for instance!
Molecular beacon
![]()
Apparatus
The fluorescence is measured with an Spectrofluorometer
Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
Application of real-time PCR to measure the initial concentration of the DNA sequence that are being amplified. As this is what's almost always done real-time PCR and qPCR are often used interchangeably.
qPCR has sensitivity that is five orders of magnitude higher than blotting techniques!
Applications
Real-Time PCR—also called quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR)—is one of the most powerful and sensitive gene analysis techniques available and is used for a broad range of applications including
- Genotyping
- genetic variation of inter and intra organisms
- Single-nucleotide polymorphism analysis / mutation analysis. See here and here. In order to distinguish the DNA of different lineages, hybridization probes were designed to recognize unique SNPs that are specific to particular lineages/sublineages.
- pathogen detection. PDF. PCR assays that discriminate between microorganisms based on a signal from specific nucleic acid sequences, for instance by SNP genotyping.
- automated diagnosis of food-borne pathogens throughout the food chain
- Diagnosing diseases like HIV, CF, Sickle cell anemia, Thalassemia, Phenyl ketonuria, etc.
- quantitative gene expression analysis. When studying gene expression with real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), scientists usually investigate changes – increases or decreases – in the expression of a particular gene or set of genes by measuring the abundance of the gene-specific transcript. The investigation monitors the response of a gene to treatment with a compound or drug of interest, under a defined set of conditions.
- drug target validation/ drug response analysis. See here
- measuring RNA interference. See Reverse transcription PCR, and here
- drug target validation/ drug response analysis. See here.
The PCR based detection technologies utilizing species- specific primers are proving indispensable as research tools. The RT PCR allows quantitative genotyping and detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms and allelic discrimination as well as genetic variation.
Real-Time PCR: Revolutionizing Detection and Expression Analysis of Genes
Frequently, real-time polymerase chain reaction is combined with reverse transcription to quantify messenger RNA (mRNA) and microRNA (miRNA) in cells or tissues. This is then called Real-time RT PCR
- Quantification of mRNA, and thus Gene expression (research and gene therapy diagnostics)
- Gene therapy distribution and expression assays
- Cell bank copy number analysis
- Expression system development
- Residual RNA analysis
- GMO analysis
- human and veterinary diagnostics
- blood products quality control
Real time vs traditional PCR In traditional PCR, Agarose gel results are obtained from the end point of the reaction, which, I think, is made up of DNA double strands