A polymer is a molecule composed of a small molecular unit repeating in a chain; usually units. The chain may have complicated topology, like branches, or cross-links. Links can also be made between different polymers (of different chemical composition for instance). These all determine the polymer architecture.
Polymer chemistry
Example of polymer: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polystyrene
Examples of polymers
- Plastics,
- Rubbers,
- Latex,
- Many Adhesives
- Many Lubcricants
- Many Viscosity Modifiers
- Conductive polymer
- Biopolymers:
Polymer architecture
Main architectures:
- Linear-chain polymer
- Branched polymers. Plastic films are somtimes branched polymers.
- Cross-linked (Polymer network)
More specific examples of architectures:
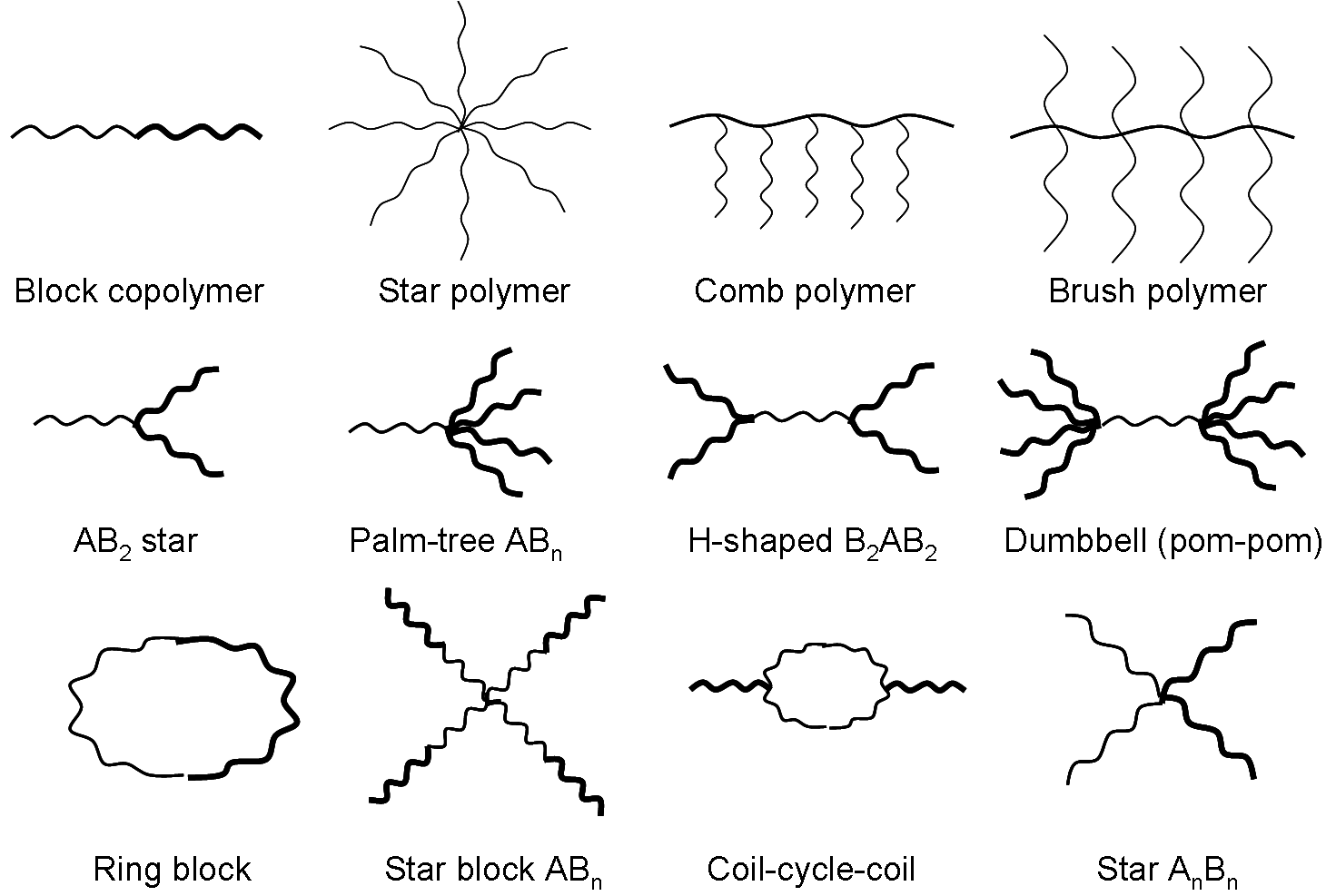
Interestingly, when one closes a linear-chain polymer into a loop, the viscosity drops dramatically.
Polymers according to synthesis reaction
Addtion polymers created by Addition reactions
Alkenes can act as monomers because they are unsaturated:
- ethene can polymerise to form poly(ethene), also called polythene
- propene can polymerise to form poly(propene), also called polypropylene
- chloroethene can polymerise to form poly(chloroethene), also called PVC
Condensation polymers created by Condensation reaction
An example of a condensation polymer is nylon, and some Proteins (the ones that are formed from repeating units)